Table of Contents
I. Introduction: Why Dry-Type Transformers Matter in Modern Critical Infrastructure
II. What Is a Dry Type Transformer?
III. Types of Dry Type Transformer
IV. Why Dry-Type Transformers Are Preferred in High-Rise Buildings
V. Dry-Type Transformers in Data Centers
VI. Offshore Installations and Marine Environments
VII. Dry Type vs Oil-Immersed Transformers: Practical Comparison
VIII. Dry Type Transformer Insulation and Its Impact on Performance
IX. Role of Dry Type Transformer Manufacturers
X. Common Misconceptions About Dry Transformers
XI. Typical Applications Summary
XII. Conclusion: Choosing the Right Dry-Type Transformer
I. Introduction: Why Dry-Type Transformers Matter in Modern Critical Infrastructure
In modern critical infrastructure, selecting the right solution is key. Dry Type Transformer Applications span high-rise buildings, data centers, and offshore installations. In environments such as high-rise buildings, data centers, and offshore installations, transformer selection directly impacts fire safety, system reliability, maintenance costs, and regulatory compliance. Among the available technologies, dry type transformers have become an increasingly preferred solution for these demanding applications.
So, what is a dry type transformer, and why are engineers, consultants, and EPC contractors choosing them over traditional oil-filled units? Simply put, a dry type transformer uses air or solid insulation systems instead of liquid dielectric oil, eliminating the risks associated with oil leakage, fire propagation, and environmental contamination.
As urban buildings grow taller, data centers become more power-dense, and offshore installations face stricter environmental regulations, dry transformers are no longer a niche product. They are now a strategic infrastructure component.
This article provides a deep technical and practical analysis of:
- What are dry type transformers and how they work
- Types of dry type transformer designs
- Benefits and limitations in real-world applications
- How dry type transformer insulation affects performance
- Why cast resin transformers dominate critical installations
- How to choose reliable dry type transformer manufacturers
The goal is not to promote one technology blindly, but to help decision-makers select the right transformer for the right environment.
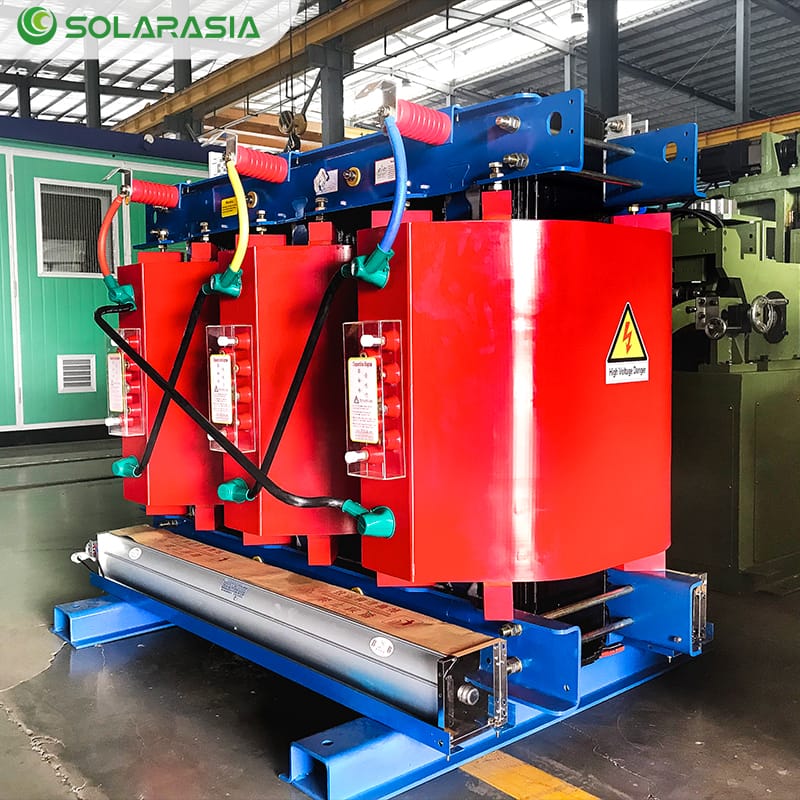

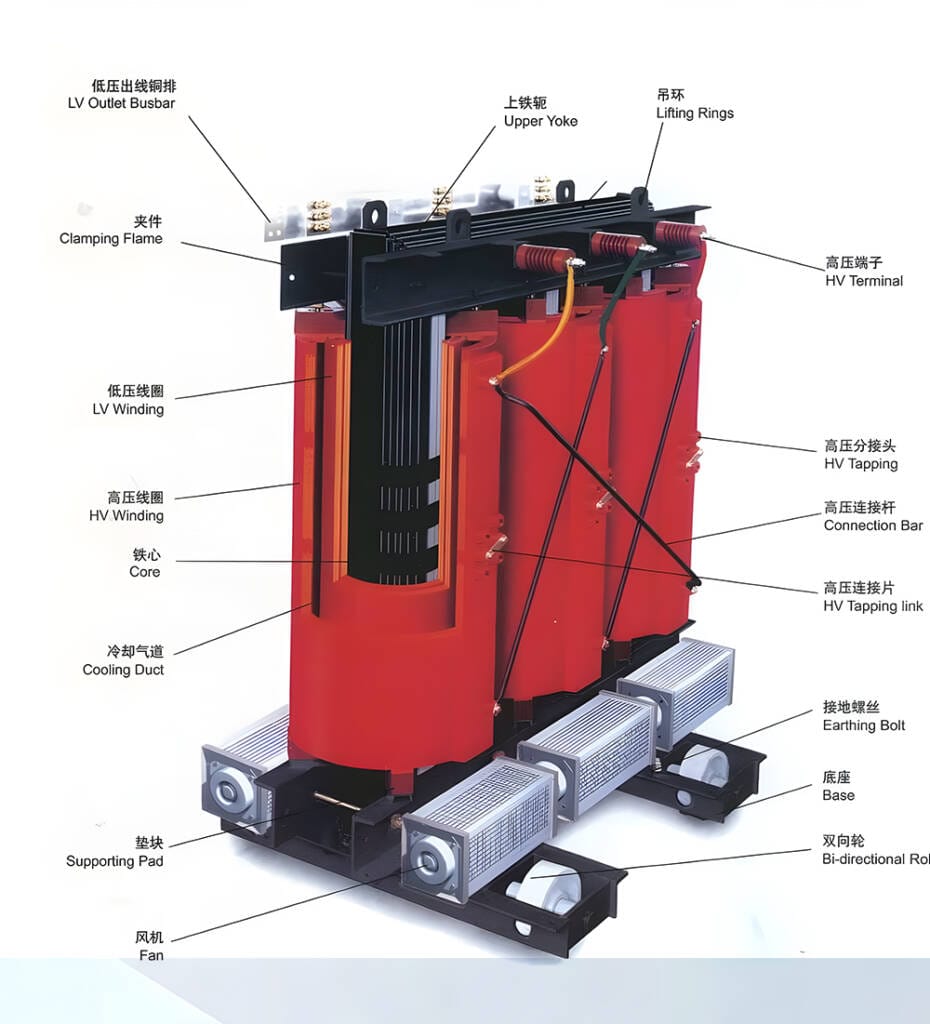
II. What Is a Dry Type Transformer?
To understand the growing adoption of dry transformers, it is important to start with a clear technical definition.
A dry type transformer is a power or distribution transformer in which the core and windings are not immersed in insulating oil. Instead, electrical insulation and thermal management rely on solid insulation materials and ambient air or forced-air cooling.
Working Principle
The fundamental electromagnetic principle is the same as any transformer:
- An alternating current in the primary winding generates a magnetic field
- The magnetic field induces voltage in the secondary winding
- Voltage transformation occurs based on turns ratio
The key difference lies in insulation and cooling.
Dry Type Transformer Insulation Systems
Dry type transformer insulation is critical to performance and longevity. Common insulation materials include:
- Epoxy resin
- Polyester resin
- Nomex paper
- Fiberglass
- Silicone-based compounds
These materials provide:
- Electrical insulation
- Mechanical strength
- Moisture resistance
- Thermal endurance
Unlike oil-filled transformers, dry type units do not rely on liquid circulation for cooling, which fundamentally changes their installation and maintenance characteristics.
III. Types of Dry Type Transformer
Understanding the different types of dry type transformer is essential for selecting the correct design for each application.
Cast Resin Transformers
Cast resin transformers are the most widely used dry type transformers in critical environments.
- Windings are encapsulated in epoxy resin under vacuum
- Excellent moisture and contamination resistance
- High mechanical strength
- Low partial discharge
These characteristics make cast resin transformers ideal for:
- High-rise buildings
- Data centers
- Hospitals
- Offshore platforms
Vacuum Pressure Impregnated (VPI) Transformers
VPI dry transformers use varnish impregnation rather than full encapsulation.
- Lower cost than cast resin
- Good thermal performance
- Less moisture resistance compared to cast resin
Often used in:
- Industrial plants
- Indoor substations with controlled environments
Open-Wound Dry Transformers
- Air-insulated windings
- Lowest cost
- Limited environmental protection
Typically applied in:
- Electrical rooms with low humidity
- Non-critical indoor installations
Dry Type Triplex Transformers
Dry type triplex transformers are commonly used in low-voltage, high-current applications, particularly in North American markets.
Key characteristics:
- Three single-phase units integrated into one assembly
- Improved load balancing
- Compact footprint
- Enhanced redundancy in certain designs
They are widely used in:
- Commercial buildings
- Data centers
- Utility distribution systems
IV. Why Dry-Type Transformers Are Preferred in High-Rise Buildings
High-rise buildings present unique electrical challenges: limited space, high occupant density, and strict fire safety codes.
Fire Safety Advantages
One of the strongest arguments for dry type transformers in high-rise buildings is fire risk reduction.
- No flammable oil
- No oil explosion risk
- Lower smoke generation
- Easier compliance with building fire regulations
In many jurisdictions, oil-filled transformers are restricted or prohibited inside tall buildings, making dry transformers the default solution.
Indoor Installation Flexibility
Dry type transformers can be installed:
- In basements
- On mechanical floors
- Close to load centers
This reduces:
- Cable length
- Voltage drop
- Power losses
Maintenance and Lifecycle Benefits
Compared to oil-filled units:
- No oil testing
- No oil replacement
- Fewer environmental inspections
- Lower long-term operational risk
Limitations in High-Rise Use
Despite their advantages, dry type transformers have limitations:
- Higher initial cost
- Larger physical size at higher ratings
- Noise management requirements
These advantages make Dry Type Transformer Applications highly suitable for high-rise building electrical rooms and mechanical floors.

V. Dry-Type Transformers in Data Centers
Data centers demand extreme reliability, making transformer selection a strategic decision.
Why Data Centers Prefer Dry Transformers
Dry type transformers are widely used in data centers because they offer:
- Improved fire safety near IT equipment
- Clean operation with no oil contamination risk
- Compatibility with indoor electrical rooms
- Easier integration with UPS systems
Thermal and Load Considerations
Data centers operate under:
- High load density
- Continuous operation
- Strict temperature control
Dry transformers must be carefully selected with:
- Adequate ventilation
- Forced air cooling if necessary
- Thermal monitoring systems
Efficiency and Redundancy
Modern dry type transformers achieve high efficiency levels and are commonly deployed in:
- N+1 redundancy configurations
- Dual-feed architectures
Limitations in Data Center Applications
- Larger footprint compared to oil-filled transformers
- Higher cost per kVA
- Cooling design complexity
When planning indoor power distribution, understanding Dry Type Transformer Applications can help engineers optimize fire safety and reliability.
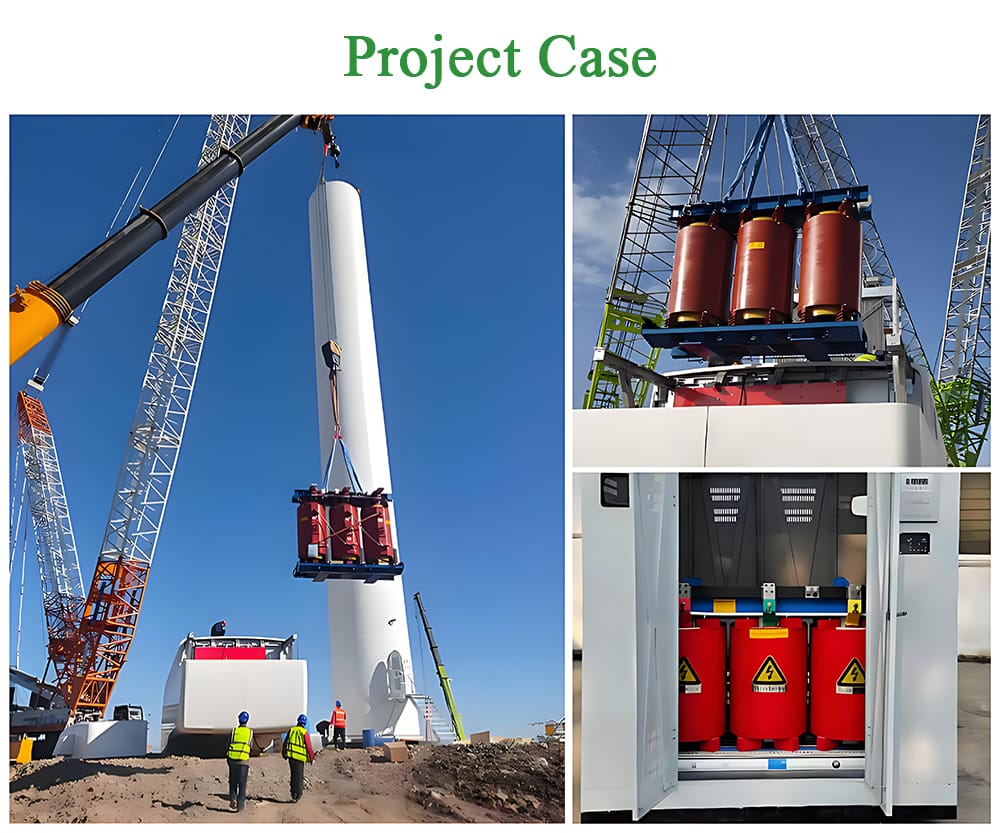
VI. Offshore Installations and Marine Environments
Offshore platforms and marine installations introduce additional challenges.
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Offshore regulations strongly discourage oil-filled equipment due to:
- Spill risks
- Environmental damage
- Cleanup costs
Dry transformers eliminate oil leakage risks entirely.
Design Enhancements for Offshore Use
Dry type transformers used offshore often feature:
- Anti-corrosion coatings
- High IP-rated enclosures
- Moisture-resistant insulation systems
- Vibration-resistant structures
Limitations Offshore
- Higher customization cost
- Cooling challenges in sealed environments
- Transport and installation constraints
VII. Dry Type vs Oil-Immersed Transformers: Practical Comparison
| Parameter | Dry Type Transformer | Oil-Immersed Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Fire risk | Very low | Higher |
| Indoor installation | Excellent | Restricted |
| Maintenance | Low | High |
| Environmental risk | Minimal | Oil leakage |
| Initial cost | Higher | Lower |
| Cooling efficiency | Moderate | High |
This comparison highlights why dry transformers dominate indoor and sensitive environments, while oil-filled units remain common outdoors.

VIII. Dry Type Transformer Insulation and Its Impact on Performance
Dry type transformer insulation determines:
- Thermal class
- Partial discharge levels
- Moisture resistance
- Service life
Common Thermal Classes
| Insulation Class | Max Temperature |
|---|---|
| Class F | 155°C |
| Class H | 180°C |
Cast resin transformers often use Class F or H insulation, making them suitable for continuous high-load operation.
IX. Role of Dry Type Transformer Manufacturers
Not all dry transformers are equal. The expertise of dry type transformer manufacturers directly affects:
- Product reliability
- Compliance with IEC / IEEE standards
- Long-term serviceability
What to Look for in Manufacturers
- Proven experience with cast resin transformers
- In-house testing facilities
- Customization capability
- Offshore and data center project references
- Global certification compliance
Leading cast resin transformers manufacturers invest heavily in:
- Resin formulation
- Vacuum casting technology
- Quality control systems
X. Common Misconceptions About Dry Transformers
- “Dry transformers require no maintenance”
→ Periodic inspection is still necessary - “Dry type transformers are always safer”
→ Proper design and installation are essential - “They can replace oil-filled transformers everywhere”
→ Not suitable for all outdoor high-capacity applications
XI. Typical Applications Summary
Dry type transformers are commonly used in:
- High-rise commercial buildings
- Hospitals and airports
- Data centers
- Offshore platforms
- Marine vessels
- Urban substations
XII. Conclusion: Choosing the Right Dry-Type Transformer
Understanding:
- What is a dry type transformer
- The types of dry type transformer
- Insulation systems
- Application-specific benefits and limitations
allows engineers and project owners to make informed decisions.
By working with experienced dry type transformer manufacturers, projects can achieve long-term operational stability and regulatory compliance in even the most demanding environments.
Choosing the right model requires understanding the benefits and limitations across different scenarios. Overall, Dry Type Transformer Applications are increasingly critical in modern industrial and commercial projects.


