Table of Contents
- Introduction: Understanding Transformer Communication Gaps
- Specification Misunderstandings: Key Transformer Communication Gaps
- Standards and Compliance: Transformer Communication Gaps in Regulatory Alignment
- Operating Conditions: Transformer Communication Gaps in Environmental Factors
- Lead Time Expectations vs Manufacturing Reality: Bridging Transformer Communication Gaps
- Testing, Inspection, and Documentation: Transformer Communication Gaps in Quality Assurance
- Logistics, Packaging, and Delivery Responsibilities: Transformer Communication Gaps in Project Execution
- How to Reduce Transformer Communication Gaps Effectively
- Why Experienced Manufacturers Make a Difference in Transformer Communication Gaps
- Conclusion and Next Steps
1. Introduction: Understanding Transformer Communication Gap
In the field of power distribution, effective communication between buyers and transformer manufacturers is critical for successful project execution. Transformer communication gaps are among the most common reasons for delays, cost overruns, and technical failures. These gaps often begin at the earliest stages of project planning, when buyers provide specifications and expectations, and continue through design, manufacturing, testing, and delivery.
A transformer is a highly engineered product. Its performance depends not only on its technical specifications but also on compliance with standards, environmental adaptation, and proper handling during transport. Misunderstandings at any stage can compromise the transformer’s reliability, safety, or efficiency.
Bridging transformer communication gaps requires awareness of where they typically occur, proactive measures from both buyers and manufacturers, and structured processes to confirm specifications, standards, environmental conditions, testing, and delivery responsibilities. This comprehensive guide explores the most frequent transformer communication gaps and offers actionable strategies for preventing them.
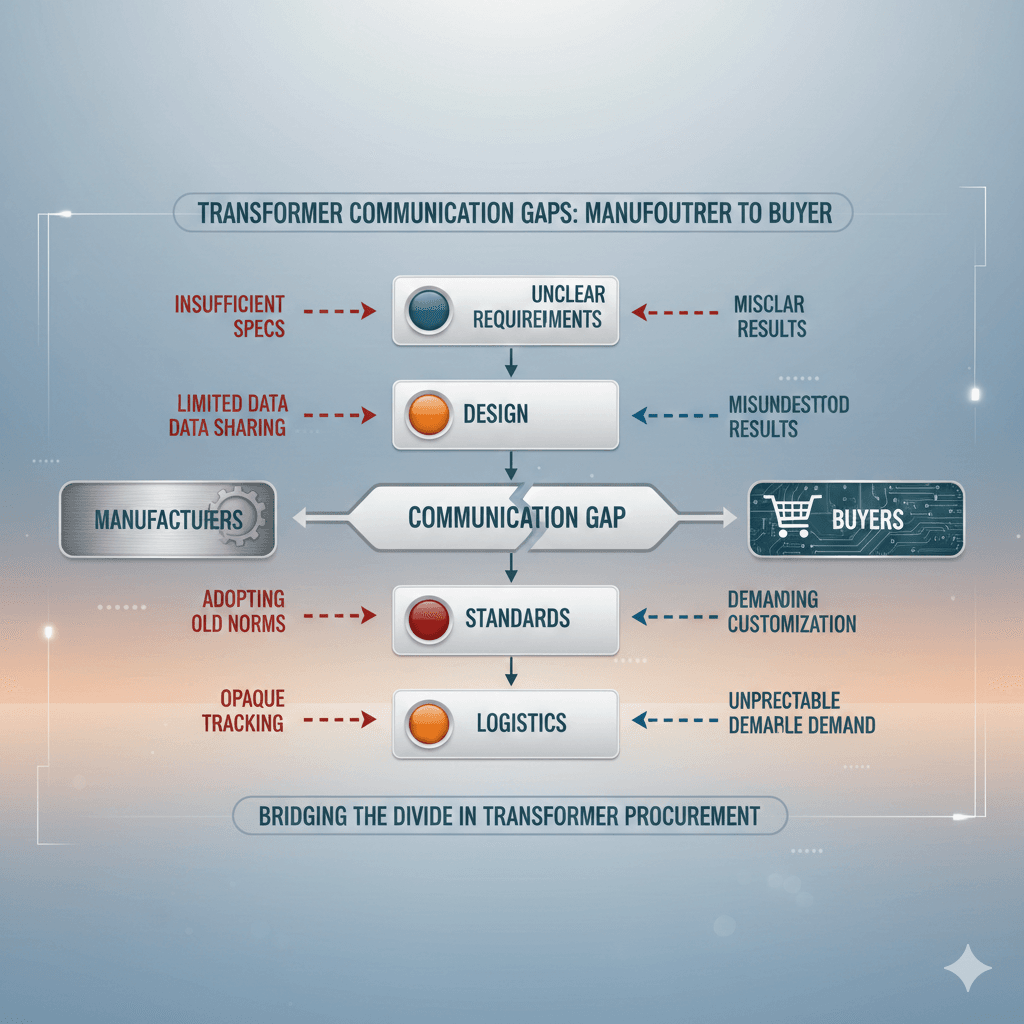
2. Specification Misunderstandings: Key Transformer Communication Gap
Specification misunderstandings are the most frequent form of transformer communication gaps. Buyers may provide only basic information such as KVA, voltage rating, and phase type, assuming these are sufficient. However, manufacturers require a detailed set of parameters to ensure the transformer meets operational, environmental, and regulatory requirements.
Key specification areas often misunderstood include:
- Load type and duty cycle: Understanding whether the load is continuous, intermittent, or peak affects transformer design and efficiency.
- Cooling methods: Natural cooling (ONAN) versus forced oil or air cooling (ONAF) impacts transformer longevity and performance.
- Installation environment: Indoor versus outdoor, altitude, temperature range, and humidity must be accurately communicated.
- Insulation and material requirements: Proper specification ensures reliability and compliance with standards.
- Regulatory compliance: Different markets may require IEC, IEEE, or ANSI standards.
| Buyer Specification | Manufacturer Expectation | Potential Risk |
|---|---|---|
| KVA and voltage only | Full operational parameters including duty cycle | Overheating, inefficiency, early failure |
| General environment notes | Specific ambient temperature, humidity, altitude | Incorrect insulation selection, reduced lifespan |
| Standard compliance mentioned | Exact standard references and test methods | Non-compliance, certification delays |
To bridge these communication gaps, buyers must provide a comprehensive technical brief, while manufacturers should proactively clarify any ambiguities. This collaboration ensures that transformers are designed correctly from the outset, minimizing project risk.
3. Standards and Compliance: Transformer Communication Gap in Regulatory Alignment
Misalignment on standards and compliance is another common source of transformer communication gaps. Buyers often assume manufacturers are fully aware of the standards required for their projects, while manufacturers may rely on default practices based on prior experience or regional norms.
Critical considerations include:
- IEC, IEEE, ANSI standards: Each has unique requirements for insulation, testing, and certification.
- Certification scope: Routine tests, type tests, and factory acceptance tests (FAT) need to be explicitly agreed upon.
- Local regulations: Different countries or regions may have additional regulatory requirements.
A common scenario involves a manufacturer designing a transformer to IEC standards when the buyer requires IEEE compliance. Without explicit communication, the transformer may fail inspection or necessitate costly modifications.
| Aspect | Buyer Assumption | Manufacturer Reality | Risk |
| Standard | Manufacturer knows local requirement | Uses default IEC | Non-compliance, project delay |
| Testing | Routine test sufficient | Type test required | Additional cost, schedule impact |
| Certification | Implicit inclusion | Requires prior agreement | Approval delays |
Proactively confirming applicable standards and test requirements early in the project significantly reduces these transformer communication gaps.
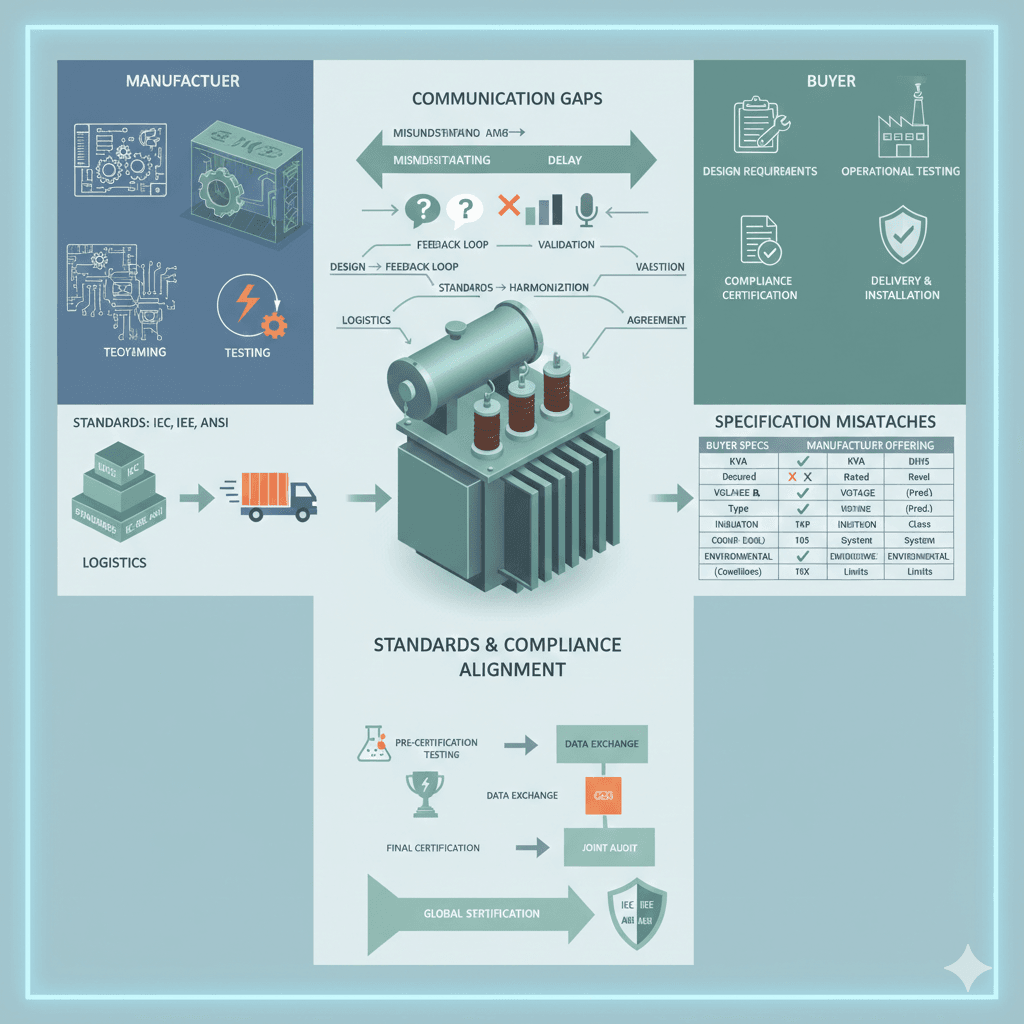
4. Operating Conditions: Transformer Communication Gap in Environmental Factors
Environmental factors are often under-communicated, creating significant transformer communication gap. Manufacturers may default to standard designs without accounting for specific site conditions, which can compromise performance and reliability.
Important environmental factors include:
- Ambient temperature and humidity: Affects insulation and cooling design.
- Altitude: Impacts dielectric strength requirements.
- Industrial pollution and coastal conditions: Influence corrosion protection.
- Indoor vs outdoor installation: Determines enclosure type, cooling, and maintenance requirements.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Transformer | Communication Requirement |
| High temperature | Overheating, reduced life | Specify maximum ambient temperature |
| High humidity | Insulation degradation | Provide relative humidity range |
| Coastal location | Corrosion risk | Indicate salt exposure |
| Dusty/industrial site | Reduced cooling efficiency | Specify particulate levels |
Accurate communication of environmental and operational factors ensures the transformer is correctly designed, reducing failures, downtime, and maintenance costs.
5. Lead Time Expectations vs Manufacturing Reality: Bridging Transformer Communication Gap
Misalignment on lead times is a frequent cause of transformer communication gaps. Buyers may assume rapid delivery for standard transformers, while manufacturers face realistic production constraints.
Factors affecting lead time:
- Design approval cycles
- Material procurement for specialized components
- Manufacturing and winding processes
- Testing and quality assurance
| Stage | Typical Duration | Buyer Expectation | Communication Gap Risk |
| Design Approval | 2–4 weeks | Immediate approval | Delay in manufacturing start |
| Material Procurement | 3–6 weeks | Off-the-shelf availability | Stock shortage, extended lead time |
| Manufacturing & Winding | 4–8 weeks | Quick production | Quality compromise if rushed |
| Testing & Inspection | 1–2 weeks | Minimal testing | Re-testing or non-compliance |
Aligning on realistic timelines early in the project reduces these transformer communication gaps and ensures smoother execution.
6. Testing, Inspection, and Documentation: Transformer Communication Gap in Quality Assurance
Testing and documentation gaps are often underestimated but critical transformer communication gaps. Misunderstandings can arise when buyers assume certain tests or reports are included by default.
Considerations include:
- Factory Acceptance Test (FAT): Buyer involvement may be required.
- Routine vs Type Testing: Scope differences affect cost and delivery.
- Documentation: Drawings, manuals, and test reports must meet language and format requirements.
| Document/Test | Buyer Assumption | Manufacturer Action | Gap Risk |
| FAT | Included automatically | Requires scheduling | Delayed acceptance |
| Type Test | Only routine test needed | Full type test performed | Additional cost, delay |
| Technical Drawings | Format optional | Manufacturer standard | Translation/rework required |
Clearly defining testing and documentation requirements from the outset bridges these gaps and ensures project success.
7. Logistics, Packaging, and Delivery Responsibilities: Transformer Communication Gap in Project Execution
Shipping, packaging, and delivery are additional sources of transformer communication gap. Misaligned expectations can lead to damage, customs issues, or installation delays.
Considerations include:
- Packaging suitable for transport method (sea, land, or air)
- Lifting points and center-of-gravity markings
- Handling, storage, and environmental protection during transit
- Responsibility for shipping, insurance, and documentation
| Aspect | Buyer Expectation | Manufacturer Responsibility | Gap Risk |
| Packaging | Standard wooden crate | Reinforced, moisture-proof | Transport damage |
| Shipping | Buyer arranges delivery | Manufacturer coordinates shipment | Delays, customs issues |
| Handling | Buyer manages lifting | Manufacturer provides lifting info | Safety incidents |
| Documentation | Only invoice | Packing list, test reports included | Customs delays |
Aligning on logistics responsibilities and communication prevents these gaps and ensures the safe delivery of transformers.
8. How to Reduce Transformer Communication Gap Effectively
Bridging transformer communication gaps requires structured processes and proactive engagement. Key strategies include:
- Comprehensive technical specification checklist
- Explicit agreement on standards, certifications, and tests
- Communication of environmental and operational conditions
- Alignment on project timelines and milestones
- Clear testing and documentation requirements
- Defined logistics and packaging responsibilities
Implementing these strategies minimizes misunderstandings, reduces project risk, and improves overall project efficiency.
9. Why Experienced Manufacturers Make a Difference in Transformer Communication Gaps
Experienced manufacturers play a vital role in bridging transformer communication gaps. They do so by:
- Proactively clarifying specifications and expectations
- Anticipating operational and environmental requirements
- Providing thorough documentation and guidance
- Leveraging cross-market experience to navigate standard and regulatory differences
Choosing an experienced manufacturer helps buyers avoid common pitfalls, ensures compliance, and improves project efficiency.
10. Conclusion and Next Steps
Transformer communication gaps are a frequent source of project delays, cost overruns, and technical failures. By understanding the most common gaps—specifications, standards, operating conditions, lead times, testing, and logistics—both buyers and manufacturers can proactively address them.
Key takeaways:
- Provide detailed technical specifications early
- Confirm applicable standards and testing requirements
- Communicate environmental conditions clearly
- Align on project timelines and milestones
- Define logistics and packaging responsibilities
Working with experienced manufacturers and following structured processes ensures transformers meet all requirements, projects remain on schedule, and risks are minimized.
Contact our team to review your transformer specifications and ensure your next project runs smoothly without communication gaps.


